Python Having User Press Enter to Continue

Get this book -> Problems on Array: For Interviews and Competitive Programming
In this article, we have explored different techniques to pause the execution of a Python Program for a specific time. There are 9 such techniques including os.pause, asyncio and much more.
Table of contents:
- Using the sleep method
- Use input function
- Using the os.pause method
- Windows mscvrt
- Awaiting Correct user Input
- Using the python interpreter functionality
- Using python asyncio
- Event.wait() method
- Timer method from threading
Python is one of the most popular programming languages. Python is used in web development,data science , system programming , devops etc. There are different instances where there is a need to pause a python program. There may be a need where we context needs to be switched or user needs to read instructions.
Using the sleep method
The python time.sleep method stops the threads execution for a few seconds
import time old = time.time() time_suspend = 5 print("****Program Starts****") time.sleep(time_suspend) print("****Program Ends****") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') In this program we print a single line but sleep the program for 5 seconds , we compare the time taken to run the program.
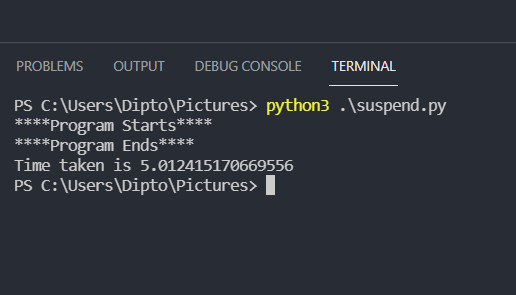
The time taken to run the program is 5.01 seconds.
If we comment out the sleep part and run the program again we can check that it runs in fewer seconds.
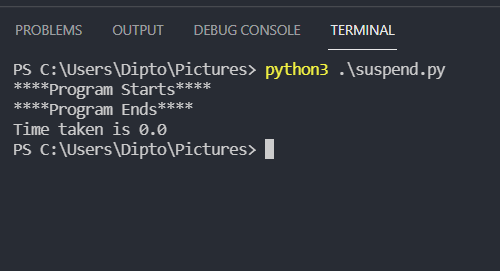
import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") print("****Program Ends****") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') The time taken in this case is
The sleep method can be used for multithreading programs also
import threading import time def print_first(): for i in range(3): time.sleep(3) print("First") def print_second(): for i in range(2): time.sleep(2) print("Second") t1 = threading.Thread(target=print_first) t2 = threading.Thread(target=print_second) t1.start() t2.start() In this program we generate two threads and execute the functions print_first and print_second which prints first and second. We use the sleep method to pause the threads so that the other thread exectues in the other duration.
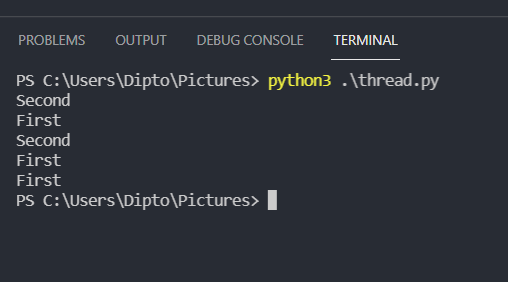
As we can see the context switches and prints in this order.
Use input function
The input function takes input in the form a line
import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") n = int(input("Enter your number : ")) print(f'Number provided is {n}') print("****Program Ends****") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') In this example we take a number input and print it , we deliberately give the input after a delay
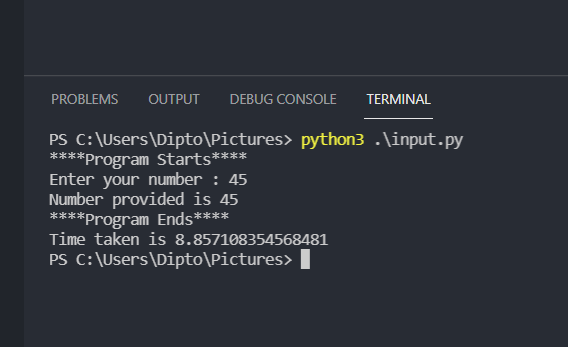
Here since we give the input in a delay it takes about 8 seconds.
Using the os.pause method
The os pause method helps pause the program execution
import os import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") os.system("pause") print("****Program Ends****") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') In this example we pause the program execution
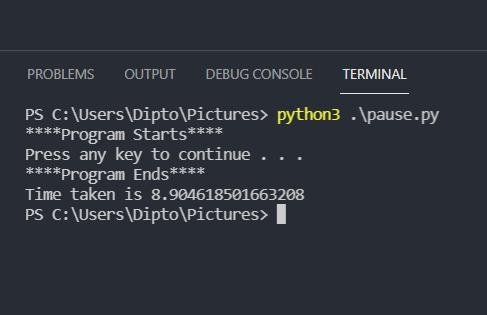
This program takes about 8 seconds as we pause the program and delay the button exit.
If we comment the pause part and check the time taken
import os import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") print("****Program Ends****") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') the time taken is considerably lesser
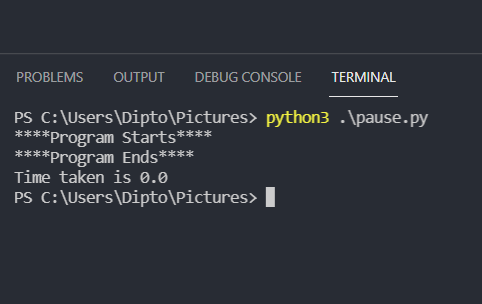
Windows mscvrt
In windows using the mscvrt can be used to force a user to await until a key is pressed and then the program proceeds. It also helps in analyzing the key pressed.
import msvcrt import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") print("Awaiting a key entry") c = msvcrt.getch() print('you entered', c) current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') The execution of this code takes the following time
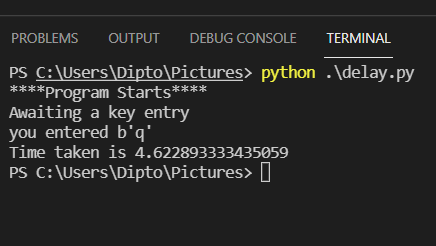
Awaiting Correct user Input
We can use an infinite loop to cause the script to run and only end the operation when a specific key is pressed by the user
import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") while True: choice = input("Enter the letter : ") if choice == 'b': print("Success") break else: print("Incorrect Key") current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') In this case the program is paused until the user enters the letter b
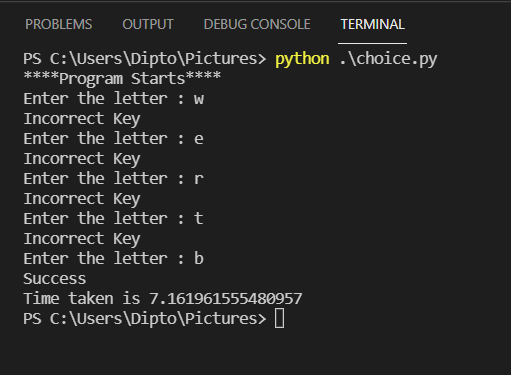
Using the python interpreter functionality
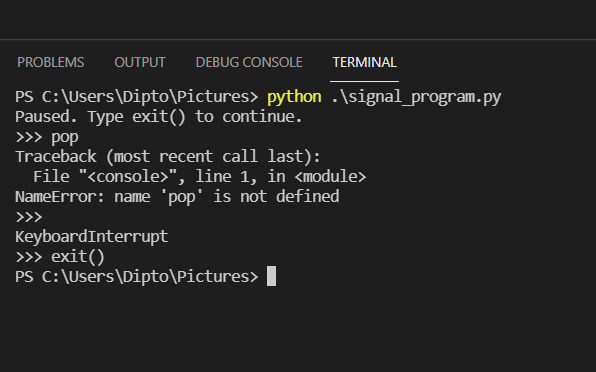
Using this we can produce an interpreter that acts almost exactly like the real interpreter, including the current context, with only the output
import code code.interact(banner='Paused. Press ^D (Ctrl+D) to continue.', local=globals()) The output is somewhat like this
Using python asyncio
The async operations can be used from python3.4 and above to do asynchronous tasks, the keywords async and await are used for this purpose
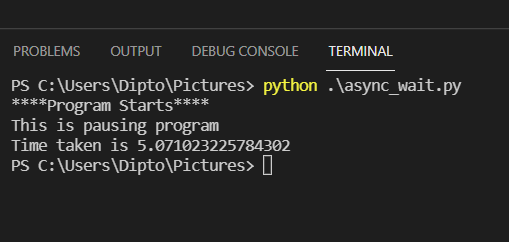
import asyncio import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") async def message(): await asyncio.sleep(5) print('This is pausing program') asyncio.run(message()) current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') In this program a message function is present which displays a message . The await functionality is used to pause the program for 5 seconds.
Event.wait() method
The Event.wait() method comes from the threading module and halts the script for a number of seconds as provided
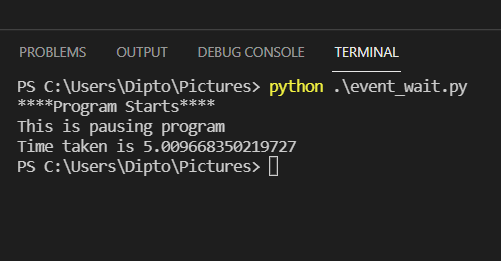
from threading import Event import time old = time.time() print("****Program Starts****") def message(): print('This is pausing program') Event().wait(5) message() current = time.time() print(f'Time taken is {current-old}') The program uses a message function to display a message and the Event.wait() is used to pause the script for 5 seconds
Timer method from threading
Similar to the previous one the timer method is another functionality from the threading package and can be used for pausing a program
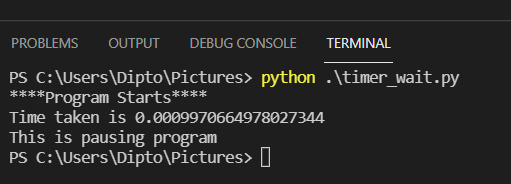
from threading import Timer def message(): print('This is pausing program') t = Timer(6,message) t.start() The program makes use of threads once again and executes
With this article at OpenGenus, you must have the complete idea of different ways we can pause a Python program.
Source: https://iq.opengenus.org/pause-python-program/
0 Response to "Python Having User Press Enter to Continue"
Postar um comentário